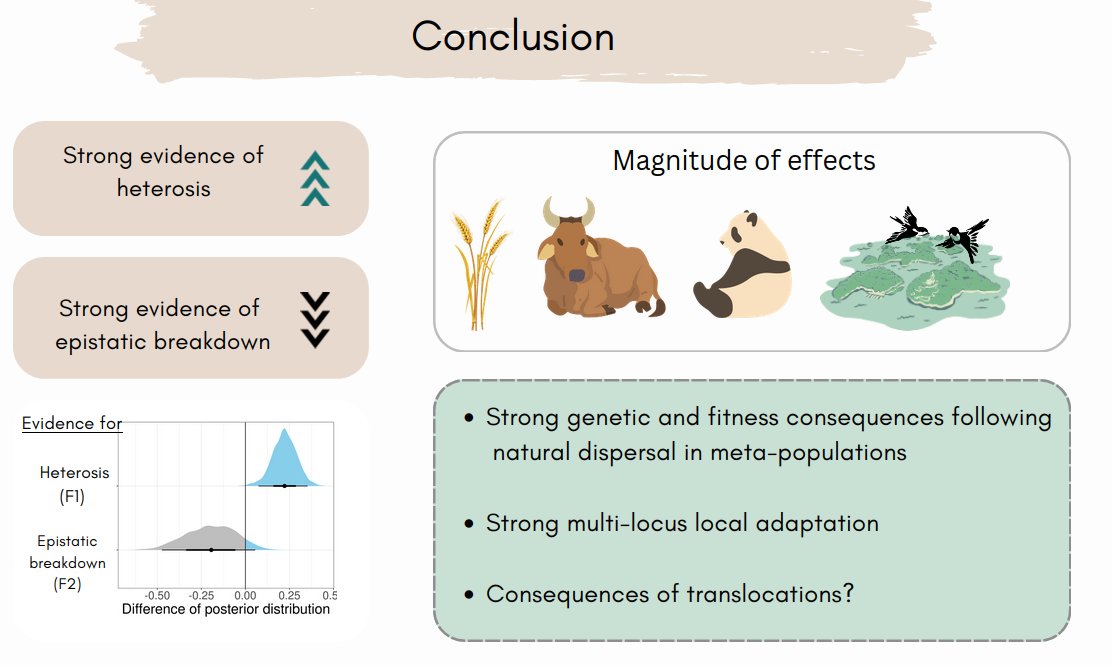
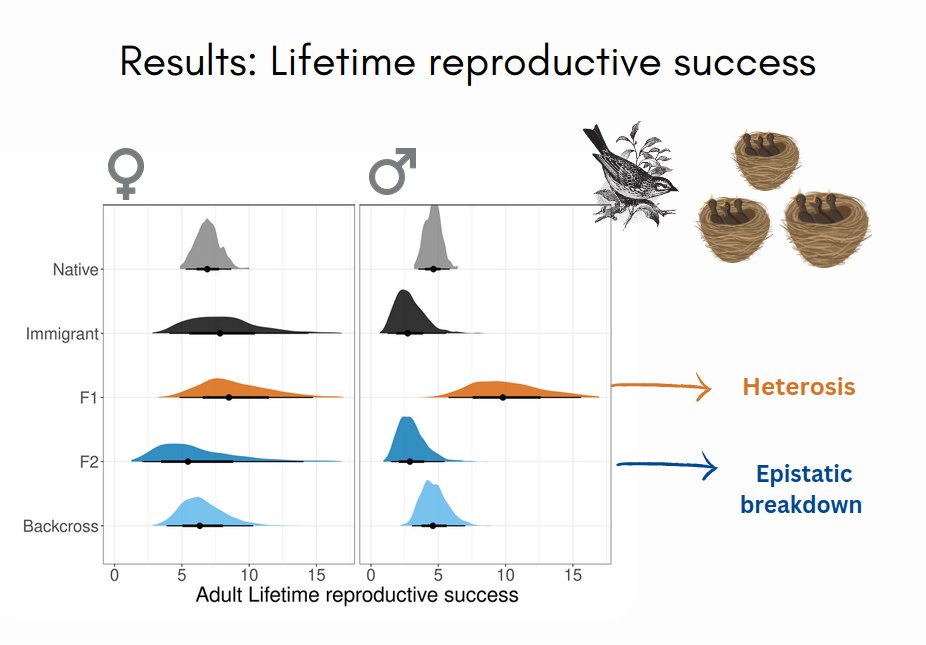
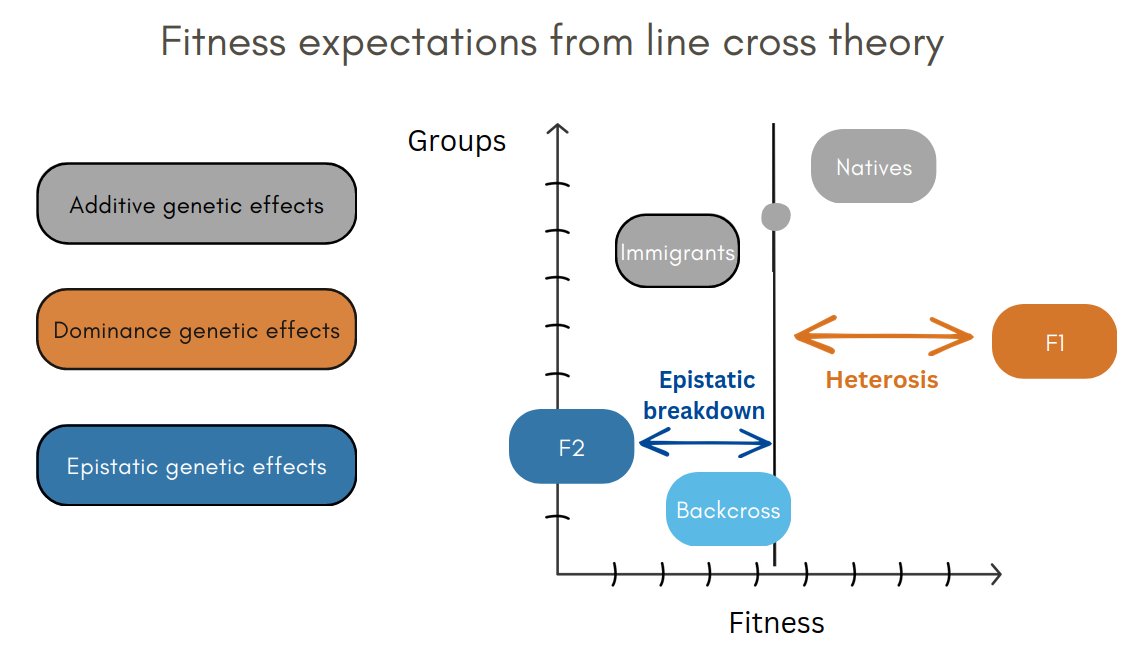
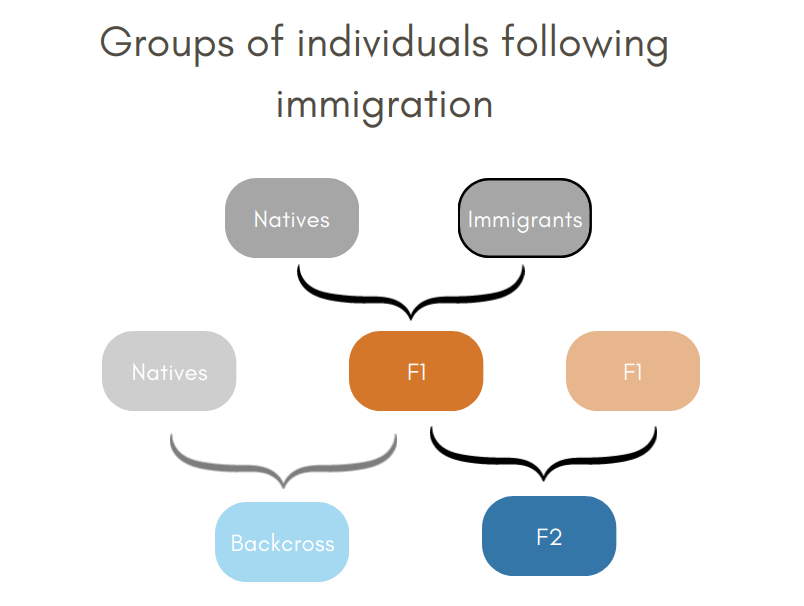
1/6 #BOU2023 #SESH4
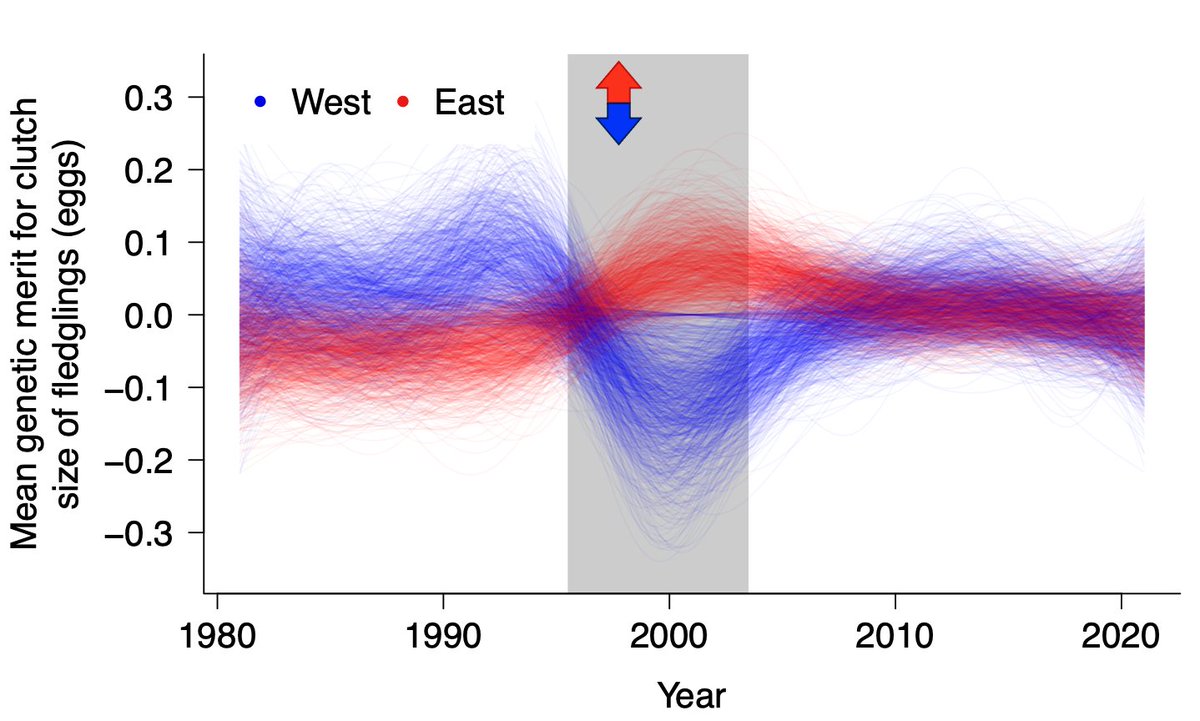
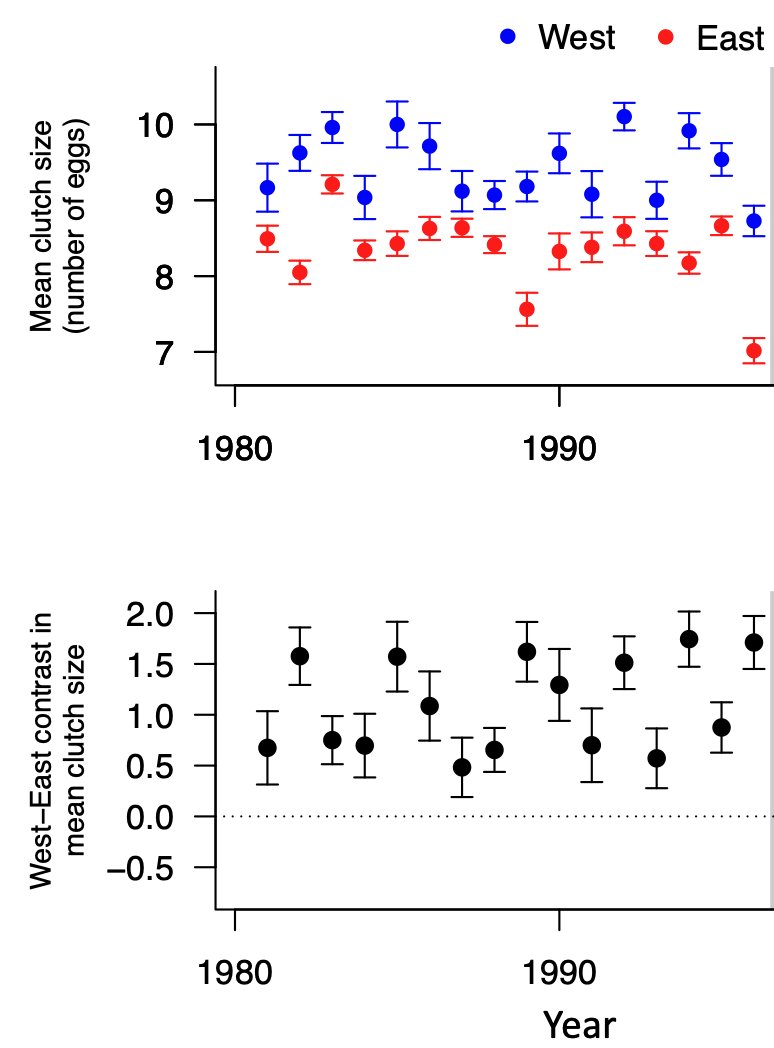
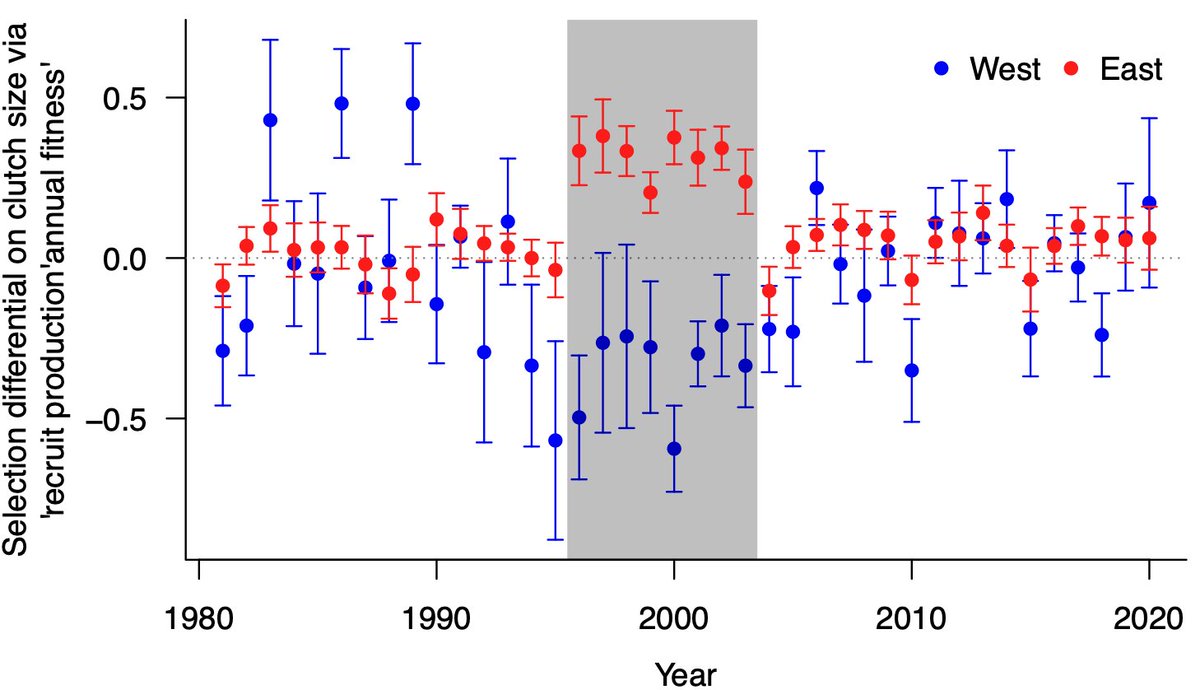
What are the genetic and fitness consequences of natural immigration in a wild meta-population?
I am a PhD candidate in evolutionary biology at CBD at NTNU @ntnu supervised by Jane Reid, Henrik Jensen, Lukas Keller, Peter Arcese and Pirmin Nietlisbach.


6/6 #BOU2023 #SESH4
This work was carried out at CBD at NTNU @ntnutogether with my supervisors and Debora Goedert, funded by NSERC / CRSNG and Norges forskningsråd. We are thankful to the Tsawout and Tseycum First Nations for allowing continuing access to X̱OX̱ DEȽ (Mandarte Island).








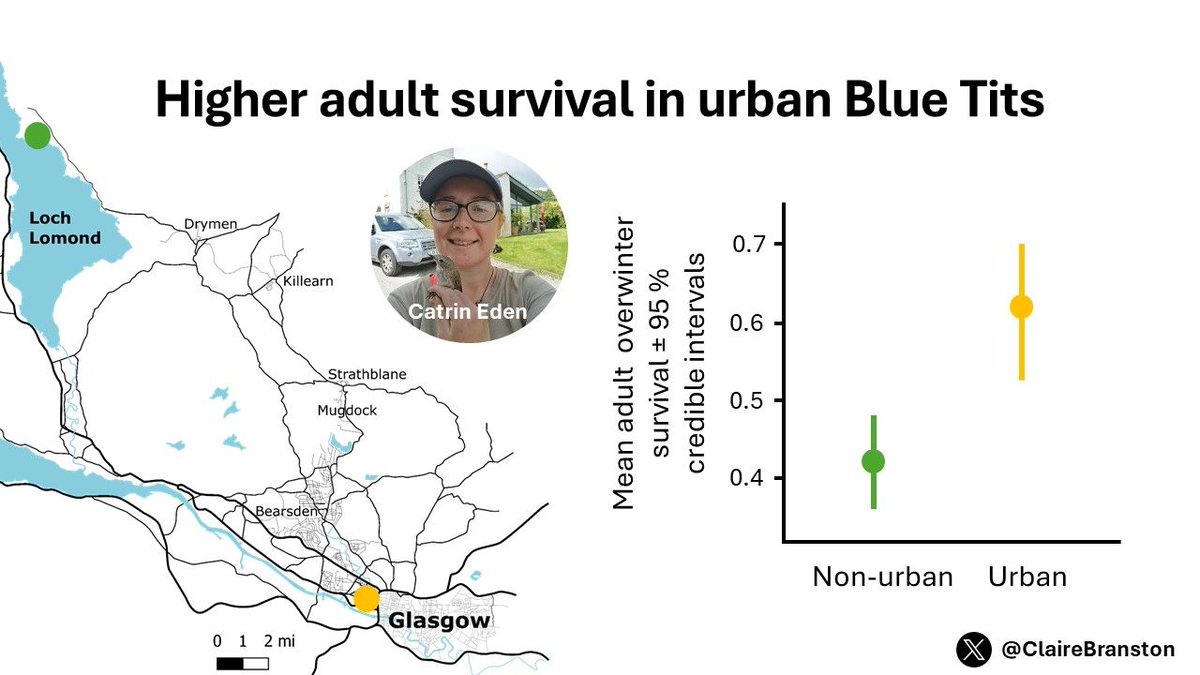
I'm excited to be at BOU Urban Birds conference #BOU2024 and to be presenting some of my recent work with Glasgow Urban Ecology Group in #SESH4 . I'll be chatting about what is driving differences in Blue Tit reproductive parameters and population growth. Come and say hi 👋 #ornithology